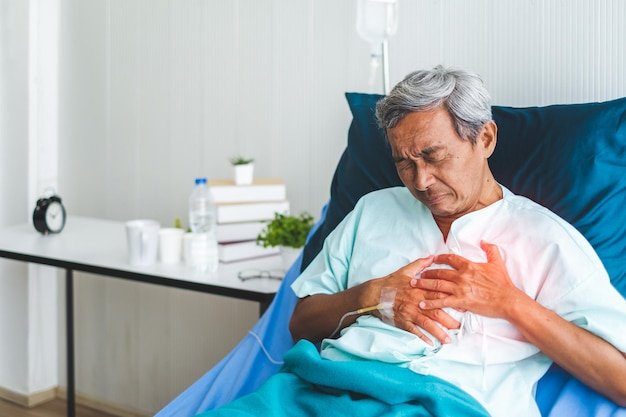
Chest tightness is a symptom that requires immediate attention. Because the chest protects the heart and lungs, any sensation of pressure, squeezing, or pain should be treated with caution. This resource is designed for educational purposes only to help you identify emergency red flags and connect you with professional medical authorities.
The Golden Rule: When in Doubt, Get Checked
Medical professionals agree that you should never try to self-diagnose chest pain at home. If you feel sudden or unexplained chest tightness, the safest action is to seek an evaluation at an Emergency Room (ER) or Urgent Care center.
Recognizing a Medical Emergency
According to the American Heart Association (AHA), certain symptoms combined with chest tightness indicate a high risk of a heart attack or other life-threatening conditions.
Call 911 or your local emergency number immediately if you experience:
- Intense Pressure: A feeling like an elephant is sitting on your chest.
- Radiation: Pain that travels to your left arm, neck, jaw, or back.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty catching your breath, even while sitting still.
- Cold Sweats: Sudden sweating paired with skin that feels cold or clammy.
- Nausea or Lightheadedness: Feeling sick to your stomach or as if you might faint.
Why Professional Diagnosis is Required
Chest tightness can stem from many different systems in the body. Only a doctor using diagnostic tools like an Electrocardiogram (ECG) or blood tests (such as Troponin levels) can determine the cause.
Common causes that require medical review include:
- Cardiac Issues: Coronary artery disease or inflammation of the heart.
- Pulmonary Issues: Blood clots in the lungs (Pulmonary Embolism) or infections like pneumonia.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Severe acid reflux (GERD) or gallbladder problems.
- Musculoskeletal Issues: Strained chest muscles or rib inflammation.
Trusted Medical Resources for Learning
To learn more about heart health and how to manage your risks, we recommend visiting these official government and health organizations:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Heart Disease Facts
- National Institutes of Health (NIH): How the Heart Works
- Mayo Clinic: Symptoms of Chest Pain
Medical Disclaimer: Life Trust Hospital Blog is a research-based information site. We do not provide medical diagnosis or treatment. The content on this page is for learning purposes only. Always consult a licensed physician for health concerns.